Generative AI vs. Large Language Models (LLMs): Key Differences
Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI are transforming business and tech.
Generative AI broadly refers to technologies capable of creating new, diverse outputs such as images, music, and synthetic data. For example, a computer designing artwork or simulating complex medical scenarios.
Large Language Models (LLMs), a subset of generative AI, focus on producing text that mirrors human writing. They learn from extensive textual data to compose anything from emails to comprehensive reports.
Generative AI and LLMs share some underlying AI principles. But their functions, applications, and implications vary significantly.
Key Differences Between Generative AI and Large Language Models
Here’s a brief summary of the main differences between generative AI and LLMs:
| Generative AI | Large Language Models | |
| Primary Function | Creates diverse types of new content | Generates human-like text |
| Data usage | Uses patterns to generate novel outputs | Analyzes extensive text data to understand and generate human-like language |
| Technology | GANs, VAEs | Transformer models |
| Examples | Text and image generation | Text generation |
| Applications | Creative industries, entertainment, content generation | Education, customer support, fraud detection |
| Ethical concerns | Copyright issues, data bias, ethical use of created content, deepfakes | Copyright issues, data bias, misinformation, academic dishonesty |
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a category of technologies that can create new, unique outputs such as images, videos, music, and text from learned data.
These systems use advanced machine learning models like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs).
This technology harnesses the power of massive datasets to produce creative and innovative results in various forms.
There are several popular generative AI tools today, including DALL-E (from OpenAI), Midjourney, and Claude (from Anthropic).
Generative AI models like ChatGPT and Midjourney can create new images based on text prompts.
Generative AI Applications
The applications of generative AI are vast and varied.
In the arts, generative AI can be used to create or supplement artwork and music compositions, offering fresh perspectives and pushing the boundaries of creative expression.
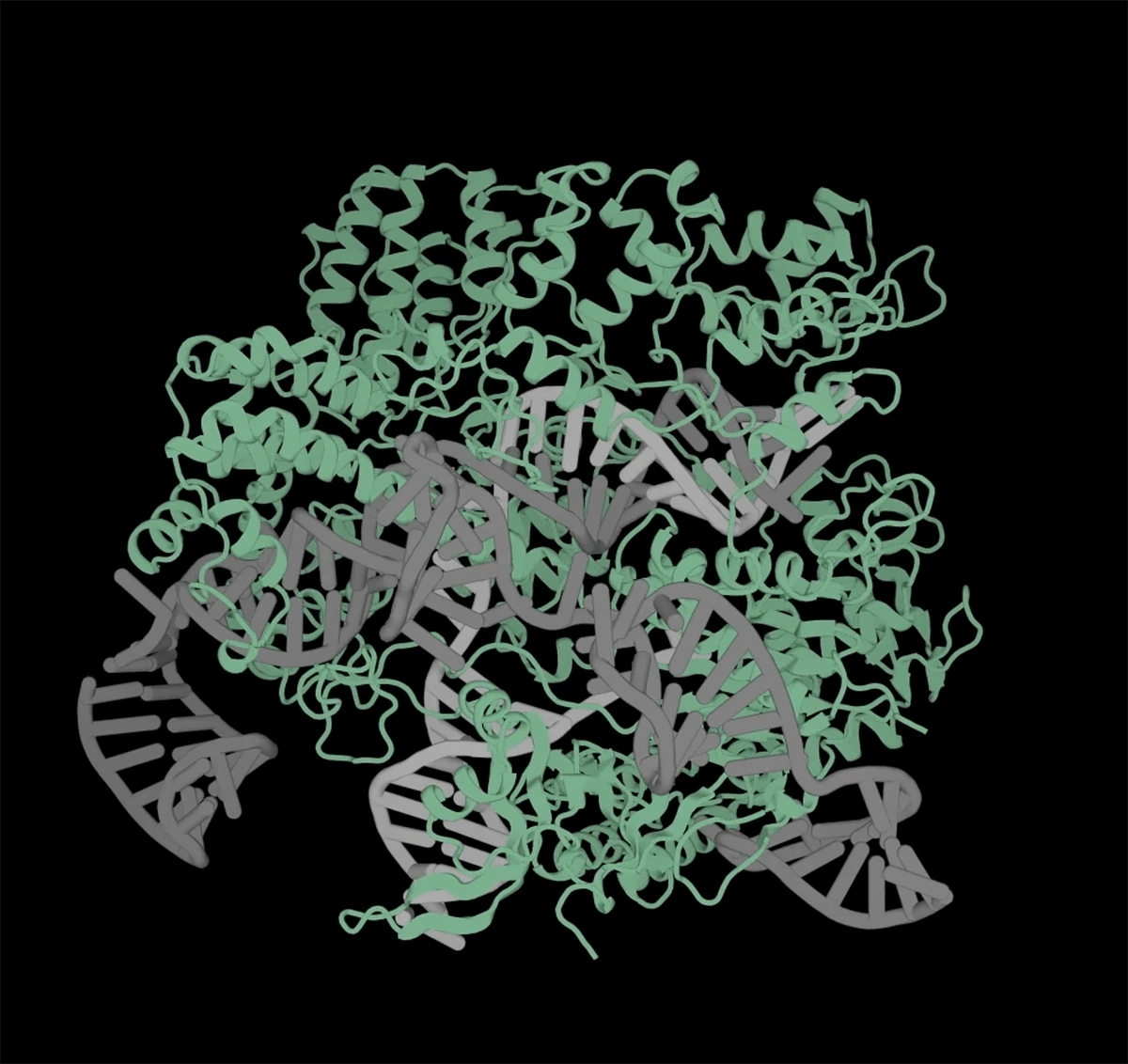
In genetics, a recent study highlights a groundbreaking application. A generative AI system, integrated with CRISPR technology, can now create new gene editors.
Structure of an AI-created gene editor. Source: Profluent
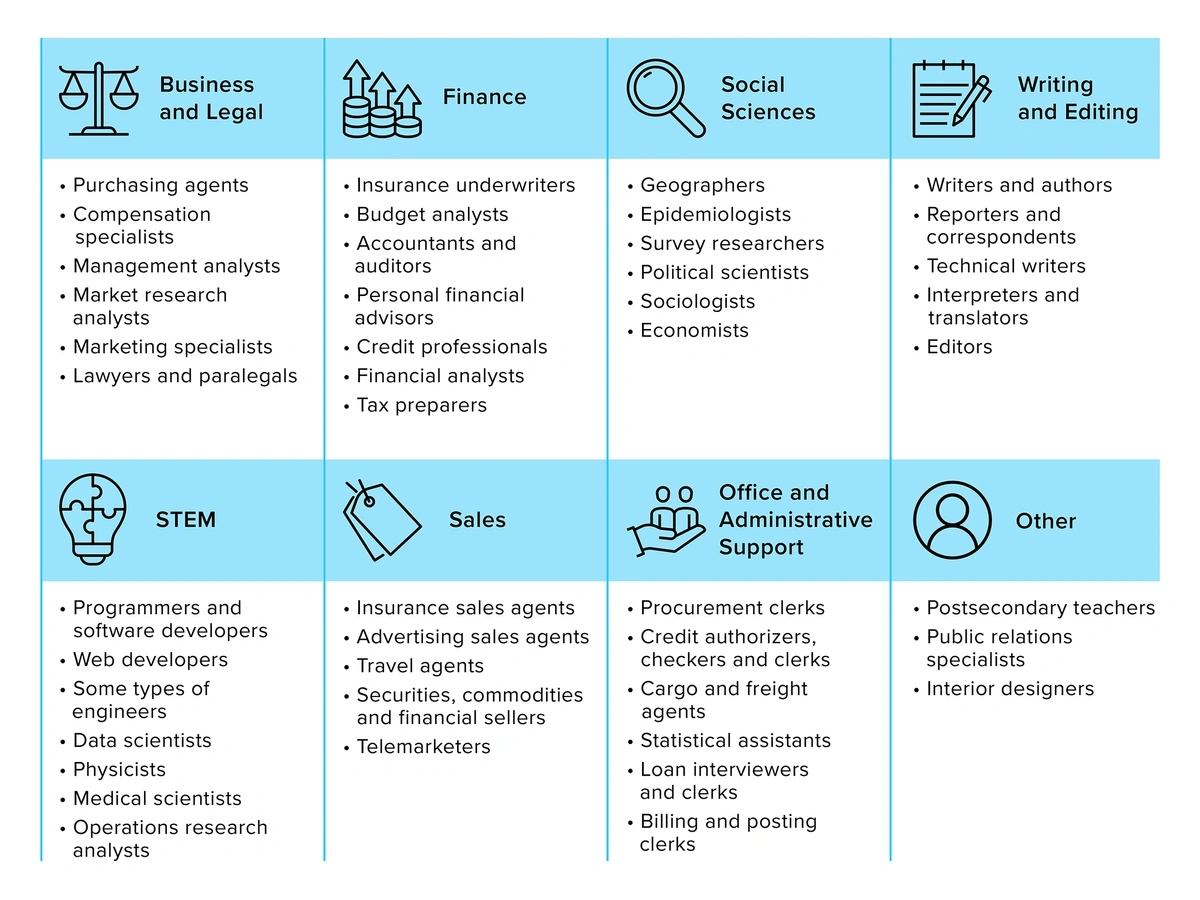
A recent report from the Burning Glass Institute and SHRM called “Generative Artificial Intelligence and the Workforce” identifies financial services, law, and marketing research as the industries most likely to be impacted by generative AI.
In financial services, generative AI can analyze market trends. In law, it can automate document standardization. For marketing professionals, it enables the creation of strategic content.
Generative AI is poised to affect multiple roles within various sectors.
Challenges of Generative AI
One major concern of generative AI is the ethical implications of deepfake technologies. Deepfakes are convincingly real videos and images that mimic real people without their consent.
Recently, a high school employee was arrested after creating a deepfake audio clip in an attempt to slander the school principal.
Copyright issues also arise as AI-generated content blurs the lines between original works and derivative creations.
Additionally, there is the threat of job displacement in various fields as generative AI technologies continue to evolve.
What are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a type of generative AI that generates human-like text.
These models, such as OpenAI's GPT or Google's BERT, leverage machine learning frameworks called transformers.
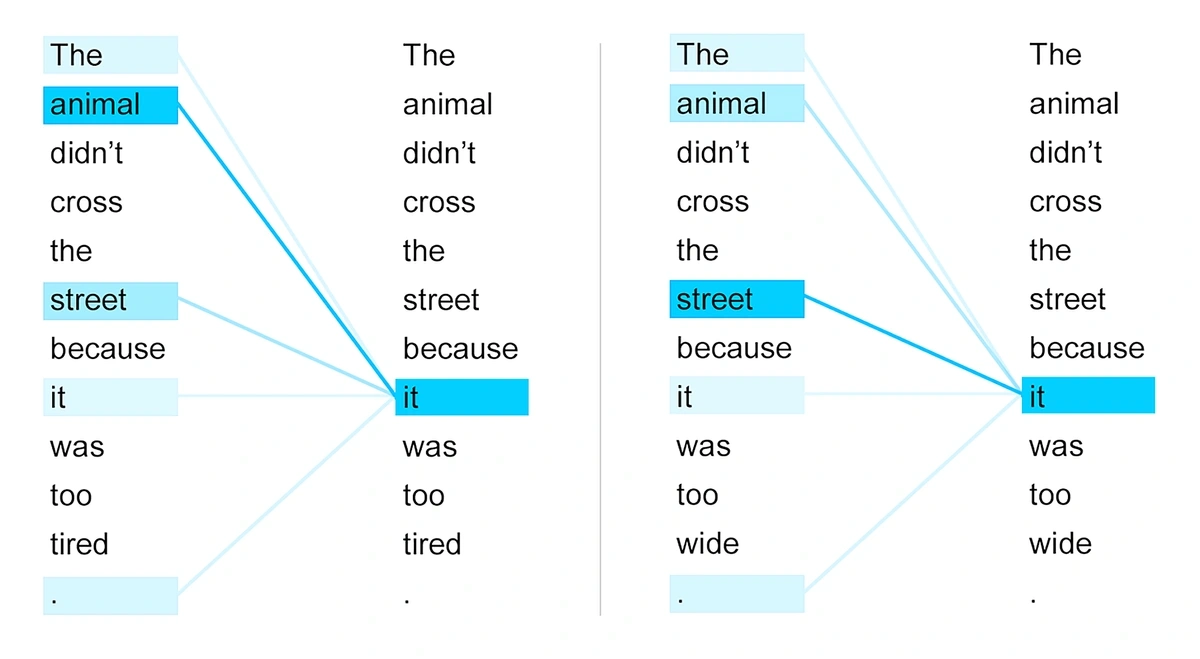
Transformers use a mechanism called self-attention. This allows the models to weigh the importance of different words relative to each other.
To do this, self-attention looks at each individual word (or partial word) in a body of text. It then determines which are most important to understanding the overall meaning.
Research from Google illustrated that self-attention could determine the meaning of “it” in different sentences. Source
A key component of how LLMs learn is through their objective function, which is the model’s overarching goal during training. In many LLMs, the objective function involves predicting the next word in a sentence given the previous words. This helps the model learn language patterns and structure.
LLMs are trained on a vast amount of textual data across many sources, such as books, Wikipedia articles, Reddit posts, and more.
This training allows them to mimic writing styles, answer questions, and broadly create contextually appropriate text across a variety of applications.
LLM Applications
LLMs have a wide range of applications.
In customer service, LLMs can automate interactions while maintaining a brand’s voice, handling everything from routine inquiries to more complex issues.
Companies like Freshworks and Zendesk incorporate AI-driven features like chatbots in their customer support services. These tools resolve customer queries and can escalate complex issues to live agents — an example of how LLMs and humans can work together to arrive at better outcomes.
Customer service companies are using generative AI to streamline and automate resolutions.
In content creation, LLMs assist writers by generating draft articles, suggesting edits, or creating entirely new pieces of content based on specified guidelines.
LLMs can also be used for fraud detection, including in the financial sector. For example, J.P. Morgan leverages LLMs for payment validation screening.
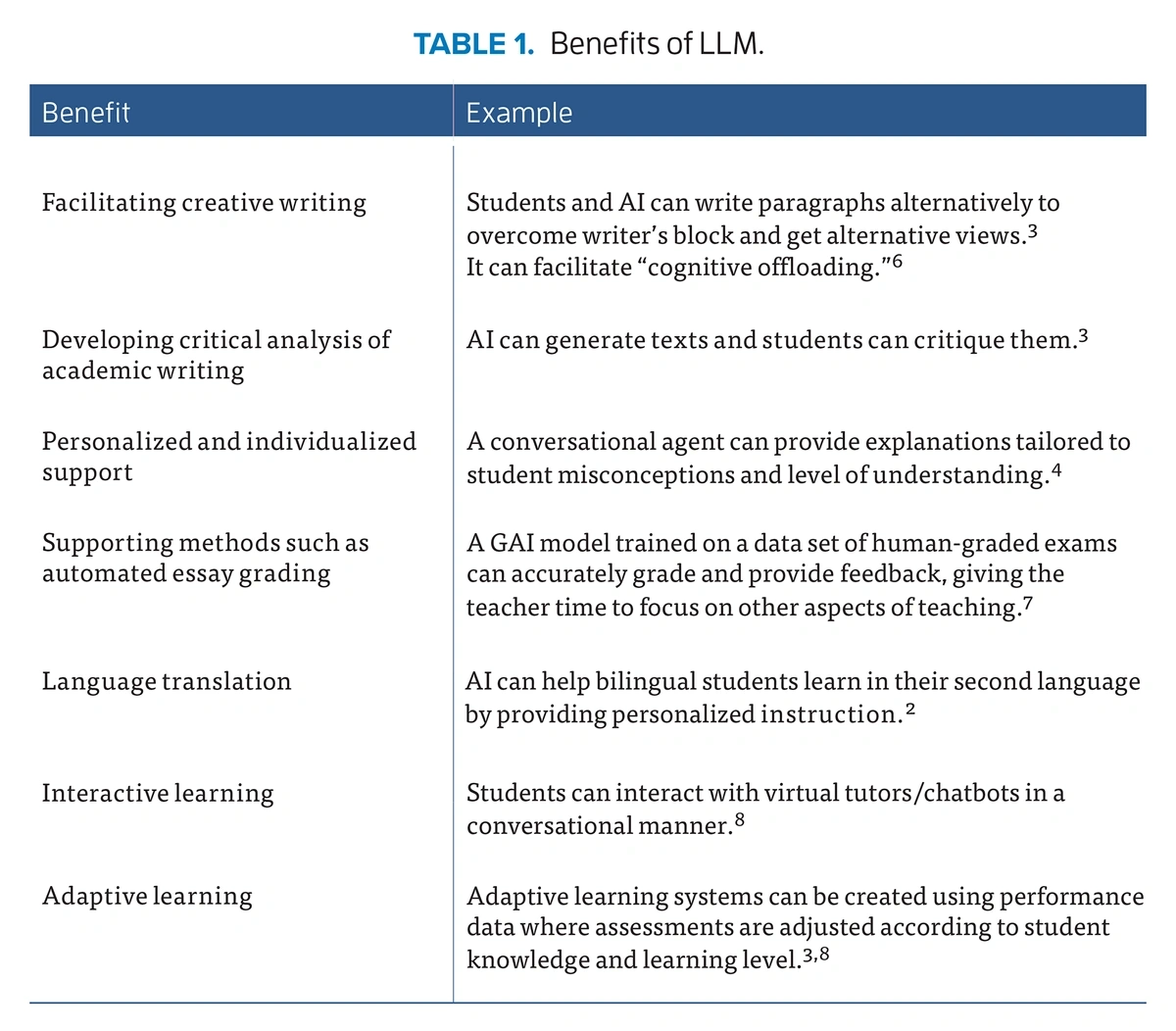
In education, teachers can use LLMs to help build lesson plans, grade assignments, and create personalized plans for students.
A few examples of how LLMs can be used in education. Source
Challenges of LLMs
LLMs pose a number of concerns.
Like broader generative AI technologies, LLMs pose significant threats to certain industries, such as finance, journalism, and customer support.
In education and academia, LLMs can enable individuals to cheat on assignments and papers. According to Nature, there have been numerous papers published in journals with the phrase “regenerate response” — indicating the text was copied from an LLM like ChatGPT.
Data bias is another major challenge, as these LLMs often replicate and amplify biases from their training data. A study published by Apple's Machine Learning Research on four different LLMs highlighted how these models are prone to stereotyping professions based on gender.
A particularly pressing legal challenge involves copyright infringement issues. LLMs typically require vast amounts of data for training, which they often get by scraping content from various sources, including copyrighted materials without explicit permission. Recently the New York Times and several other US newspapers sued OpenAI and Microsoft for copyright infringement, highlighting the complex ethical and legal landscape that surrounds LLMs.
LLMs also can generate and spread misleading or false information, posing risks to information integrity and public trust.
Generative AI vs. LLMs Recap
Generative Capabilities
Both Generative AI and LLMs are capable of generating new content.
Generative AI can produce a variety of content types like images, videos, and text.
LLMs are a subset of generative AI that specializes in generating coherent, contextually relevant text.
Core Technologies
Generative AI uses technologies like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs). These models learn to create new outputs by mimicking the distribution of input data.
LLMs (Large Language Models) use transformer models. Transformers use self-attention to weigh the relevance of all parts of the text to each other. This makes LLMs effective for tasks that require a deep understanding of language.
Data Usage
Generative AI models require diverse and large datasets to effectively create new content.
LLMs specifically require large volumes of high-quality text data.
Application Areas
Generative AI has broad applications across many industries, including creative fields, science, finance, and more.
LLMs excel in environments that demand high levels of text interaction, such as customer support systems and educational tools. Additionally, LLMs are used in industries like finance for tasks like fraud detection, where they analyze textual data to identify anomalies.
Ethical and Practical Challenges
Both LLMs and Generative AI deal with data bias and copyright concerns due to their reliance on extensive datasets.
Generative AI poses unique challenges with the potential creation of deepfakes.
LLMs have been criticized for enabling academic dishonesty and potentially spreading misinformation due to their ability to generate convincing textual content.
Final Thoughts
Generative AI encompasses a broad range of technologies, including Large Language Models (LLMs).
While generative AI as a whole pushes the boundaries of creative content production, LLMs specifically refine how we generate and interact with textual data.
The integration of these technologies into various sectors brings transformative potential but also poses significant ethical challenges and risks.
By understanding the specific roles and capabilities within the broader spectrum of generative AI, we can better navigate these technologies and use them effectively.